Introduction:
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside the ovaries. They are relatively common among women of all ages, especially during their reproductive years. In most cases, ovarian cysts are harmless and don’t cause significant symptoms. However, some can lead to discomfort and complications if left untreated. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and available treatments for ovarian cysts is crucial for women to maintain optimal health.
At Saukhyam Hospital, we provide expert care and personalized treatment options for women experiencing issues related to ovarian cysts. Our team of skilled gynecologists is dedicated to offering comprehensive care, from diagnosis to treatment, ensuring that every patient is given the highest standard of medical attention.
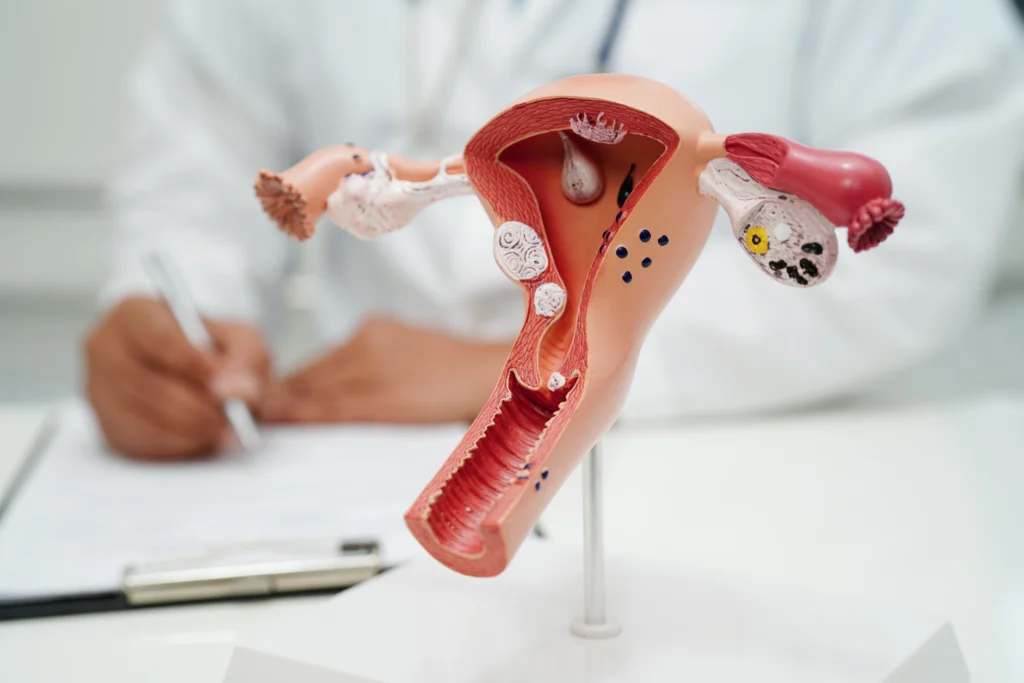
What is an Ovarian Cyst?
An ovarian cyst is a sac filled with fluid that forms on the ovaries. These cysts can vary in size, from a tiny pea to several inches in diameter. The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system and are responsible for producing eggs. Ovarian cysts are typically classified into two types:
- Functional cysts: These are the most common type and are usually harmless. They form as part of the normal menstrual cycle and typically go away on their own after a few menstrual cycles.
- Pathological cysts: These are less common and may be caused by abnormal cell growth. Some pathological cysts can become large and cause complications, while others may require surgical removal.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
While many ovarian cysts are asymptomatic and do not cause noticeable symptoms, some women may experience signs or discomfort, especially if the cyst becomes large or ruptures. Symptoms can vary depending on the type and size of the cyst. Common symptoms include:
- Pelvic pain: This is one of the most common symptoms of an ovarian cyst. The pain may be sharp or dull and can be felt in the lower abdomen or pelvic region. The pain may be constant or may vary depending on the time of the menstrual cycle.
- Bloating or heaviness: Some women may feel bloated or a sense of fullness in the abdomen. This can occur even if the cyst is small and may worsen with the passage of time.
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Ovarian cysts can sometimes affect the regularity of a woman’s menstrual cycle. This may include missed periods or bleeding between periods.
- Pain during intercourse: Painful sexual intercourse is another potential symptom of ovarian cysts. The discomfort can vary depending on the position or depth of penetration.
- Urinary issues: If the cyst is large, it may put pressure on the bladder, leading to frequent urination or a constant feeling of needing to urinate.
- Nausea and vomiting: In more severe cases, if a cyst ruptures or twists, it can cause significant abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. These are signs that immediate medical attention is required.
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
It’s important to seek medical care if you experience severe or sudden pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, especially if it is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, or fever. These symptoms may indicate a ruptured cyst or ovarian torsion, both of which require immediate medical attention. Additionally, any changes in your menstrual cycle, such as unusually heavy bleeding or missed periods, should also be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts form when a follicle (a sac that contains an egg) fails to release an egg or does not break open properly during the menstrual cycle. This can lead to the formation of a cyst. However, there are several factors that can contribute to the development of ovarian cysts:
- Hormonal imbalances: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly an imbalance in the reproductive hormones estrogen and progesterone, can increase the likelihood of ovarian cyst formation. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) are often associated with hormonal imbalances that cause multiple cysts to develop on the ovaries.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside it. This tissue can attach to the ovaries and lead to the formation of cysts called endometriomas.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the body produces hormones that can cause a cyst to form. Sometimes, the cyst will resolve on its own as the pregnancy progresses.
- Previous ovarian cysts: Women who have had ovarian cysts in the past may be more prone to developing them again. If the cysts are not monitored or treated, they may reappear over time.
- Infections: Pelvic infections or sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can increase the risk of ovarian cyst formation. These infections can spread to the ovaries and cause inflammation, leading to cyst formation.
- Age: Ovarian cysts are most common in women of reproductive age, particularly between 20 and 40. After menopause, the likelihood of developing cysts decreases, but some postmenopausal women may still be at risk, especially if they are taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT).
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk of ovarian cysts, especially in women with PCOS, as hormonal imbalances are more common in obese individuals.
Risk Factors for Ovarian Cysts:
While ovarian cysts can develop in any woman, certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing them:
- Age: Women of reproductive age are more likely to develop ovarian cysts. However, women approaching menopause are also at risk, especially if they are undergoing hormone therapy.
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome): Women with PCOS often have multiple cysts on their ovaries and experience irregular menstrual cycles, making them more prone to developing ovarian cysts.
- Family history: A family history of ovarian cysts or ovarian cancer may increase a woman’s risk of developing ovarian cysts.
- Pregnancy: Ovarian cysts are more common during pregnancy as the body undergoes hormonal changes.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts:
If you are experiencing symptoms of ovarian cysts, it’s important to seek medical advice. At Saukhyam Hospital, we offer advanced diagnostic tools to help detect and evaluate ovarian cysts:
- Pelvic ultrasound: This imaging test is the most common method for diagnosing ovarian cysts. It uses sound waves to create an image of the ovaries and can help determine the size, location, and type of cyst.
- CT scan or MRI: In some cases, a CT scan or MRI may be used to provide a more detailed image of the ovaries and surrounding organs.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help determine if there is an underlying issue such as an infection or hormone imbalance. In some cases, a blood test can also help rule out ovarian cancer, particularly if the cyst appears suspicious.
Treatment for Ovarian Cysts:
The treatment for ovarian cysts depends on their size, type, and whether they are causing symptoms. Many cysts resolve on their own without the need for medical intervention. However, if the cyst is large, painful, or has the potential to cause complications, treatment options may include:
- Watchful waiting: In many cases, especially with functional cysts, doctors may recommend monitoring the cyst with regular ultrasounds to see if it resolves on its own. This approach is often recommended for cysts that are small and not causing significant symptoms.
- Medications: Birth control pills may be prescribed to help regulate the menstrual cycle and prevent the formation of new cysts. In some cases, hormone therapy may be recommended to balance hormonal fluctuations that contribute to cyst formation.
- Surgical removal: If the cyst is large, causing pain, or has the potential to cause complications, surgery may be necessary. This can be done through traditional surgery or laparoscopic surgery, which involves smaller incisions and faster recovery times.
- Ovarian cystectomy: If the cyst is large or is located in a place that makes it difficult to remove, an ovarian cystectomy (removal of the cyst without removing the ovary) may be recommended.
- Hysterectomy: In rare cases where the cysts are recurrent or associated with a more serious underlying condition, such as ovarian cancer, a hysterectomy (removal of the ovaries and uterus) may be necessary.
Preventing Ovarian Cysts:
While not all ovarian cysts are preventable, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce your risk of developing them. Some prevention tips include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Regular exercise and a balanced diet can help prevent hormonal imbalances and reduce the risk of ovarian cysts.
- Managing underlying conditions: If you have PCOS or endometriosis, managing these conditions with the help of your doctor can reduce your risk of developing cysts.
Regular check-ups: Regular gynecological exams and ultrasounds can help detect ovarian cysts early, allowing for prompt treatment and minimizing complications.
Conclusion:
Ovarian cysts are common and, in most cases, benign. However, it is essential to recognize the symptoms and seek medical advice if you experience any discomfort or changes in your menstrual cycle. At Saukhyam Hospital, our team of experienced gynecologists is here to provide accurate diagnoses and personalized treatment options to help manage ovarian cysts. If you suspect you have an ovarian cyst, don’t hesitate to book a consultation with us. We are committed to providing compassionate care for women’s health at every stage of life.
Call us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step toward better health.

